- Project: Analysis Device Sample Cooling
- Cooling Approach: Free Piston Stirling Cooler
- Demand: A scientific lab in Australia is building a new analysis machine for tritium measurement in groundwater samples and is interested in using RIGID company Stirling coolers with KF flanges in their design. It would be used to attach the coolers to their water vapor trap apparatus, which is designed to remove water vapor from gas samples passing through a cold chamber at low pressure.
- Recommended product: Stirling Cryocooler RS100-PLUS
Get A Sample Online
Background
The customer (Australian Scientific Lab) is in the process of developing a new analysis machine dedicated to measuring tritium levels in groundwater samples. As part of their design, they have opted to incorporate Stirling coolers, specifically the RS100 PLUS model. Stirling coolers, also known as Stirling cryocoolers, play a crucial role in achieving and maintaining low temperatures for various scientific applications. In this context, they serve as a key component to ensure the success and accuracy of tritium measurements.
The primary function of the Stirling cooler in this application is cryogenic cooling. Tritium analysis often demands extremely low temperatures, and Stirling coolers are well-suited for achieving and maintaining these conditions. Capable of reaching temperatures below -100 degrees Celsius, the RS100PLUS model provides the necessary cold environment required for precise tritium measurements. The ability to establish such low temperatures is essential for enhancing the sensitivity and accuracy of analytical instruments.
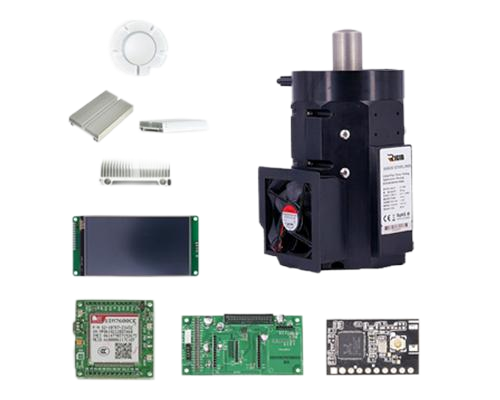

Free Piston Stirling Cooler – RS100 PLUS

Stirling RS100 Plus with Flange KF50
Analysis Machine Cooled by Cryocooler, No Liquid Nitrogen.
Besides tritium measurement analysis, RIGID company Stirling Crycoolers are often sought for various measurement and analysis devices across different scientific and industrial domains. Here are some measurement analysis devices that may utilize Stirling Cryocoolers:
- High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Detectors:
Stirling coolers can be incorporated into detectors for HPLC systems, ensuring stable and low temperatures for improved detection sensitivity in chromatographic analyses. - Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) Systems:
In GC-MS instruments, Stirling coolers may be employed to cool components such as the mass spectrometer, enhancing the precision and accuracy of chemical analyses. - Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectrometers:
Stirling coolers are used to cool the magnets in NMR spectrometers, maintaining low temperatures for optimal performance and signal resolution in nuclear magnetic resonance experiments. - Fluorescence Spectrometers:
Instruments used for fluorescence spectroscopy, which measures the emission of light from a sample, may benefit from Stirling coolers to enhance signal-to-noise ratios and improve sensitivity. - Cryopumps:
Stirling coolers are employed in cryopumps used for creating and maintaining vacuum environments in various applications, such as in mass spectrometry systems. - Environmental Gas Analyzers:
Devices for analyzing gases in the environment, such as air quality monitoring equipment, may use Stirling coolers to maintain stable temperatures for accurate measurements. - Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEMs):
In some SEMs, Stirling coolers can be utilized to cool the detectors and other components, ensuring high-resolution imaging by reducing thermal noise. - Atomic Force Microscopes (AFMs):
Stirling coolers may be integrated into AFMs to cool the scanning tips or other sensitive components, enhancing the precision of surface imaging and measurements. - High-Resolution Mass Spectrometers:
Mass spectrometers with high-resolution capabilities, used in fields such as proteomics and metabolomics, may benefit from Stirling coolers to maintain optimal operating temperatures. - Infrared (IR) Spectrometers:
Stirling coolers can be employed in IR spectrometers, which analyze the absorption of infrared radiation by molecules, to enhance the sensitivity of the measurements. - X-ray Crystallography Systems:
Instruments used for X-ray crystallography, a technique for determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal, may use Stirling coolers to cool detectors and other components. - High-Speed Cameras:
Some high-speed cameras utilized in scientific research or industrial applications may incorporate Stirling coolers to cool the sensors, ensuring optimal performance during high-speed imaging.
These examples showcase the diverse applications of Stirling coolers in measurement and analysis devices across various scientific disciplines, demonstrating their versatility in maintaining precise and stable temperatures for accurate data acquisition.

Analysis Machine Directly Cooled by Cryocooler – RIGID
Cryocooler Working Principle
- Cryogenic Cooling: Stirling coolers can achieve very low temperatures, often below -100 degrees Celsius. This is crucial for certain scientific applications, such as the analysis of tritium in groundwater samples, which may require extremely low temperatures for accurate measurements.
- Precision Temperature Control: Stirling coolers offer precise temperature control, ensuring that the analysis machine can maintain a stable and controlled temperature environment. This is essential for accurate and reproducible measurements in scientific experiments.
- Compact and Vibration-Free Operation: Stirling coolers are known for their compact size and vibration-free operation. This is advantageous in laboratory settings where space is often limited, and minimizing vibrations is crucial for sensitive measurements.
- Reliability: Stirling coolers are known for their reliability and long operational life. This is important for continuous and prolonged use in scientific experiments and analysis.
Regarding how the cryocooler works in this application, Stirling coolers operate on the Stirling cycle, a thermodynamic cycle that involves the compression and expansion of a gas (typically helium) to achieve cooling. The basic steps include compression of the gas, transfer of heat away from the gas, expansion of the gas, and then the transfer of heat back into the gas. This cycle allows the Stirling cooler to achieve and maintain low temperatures.
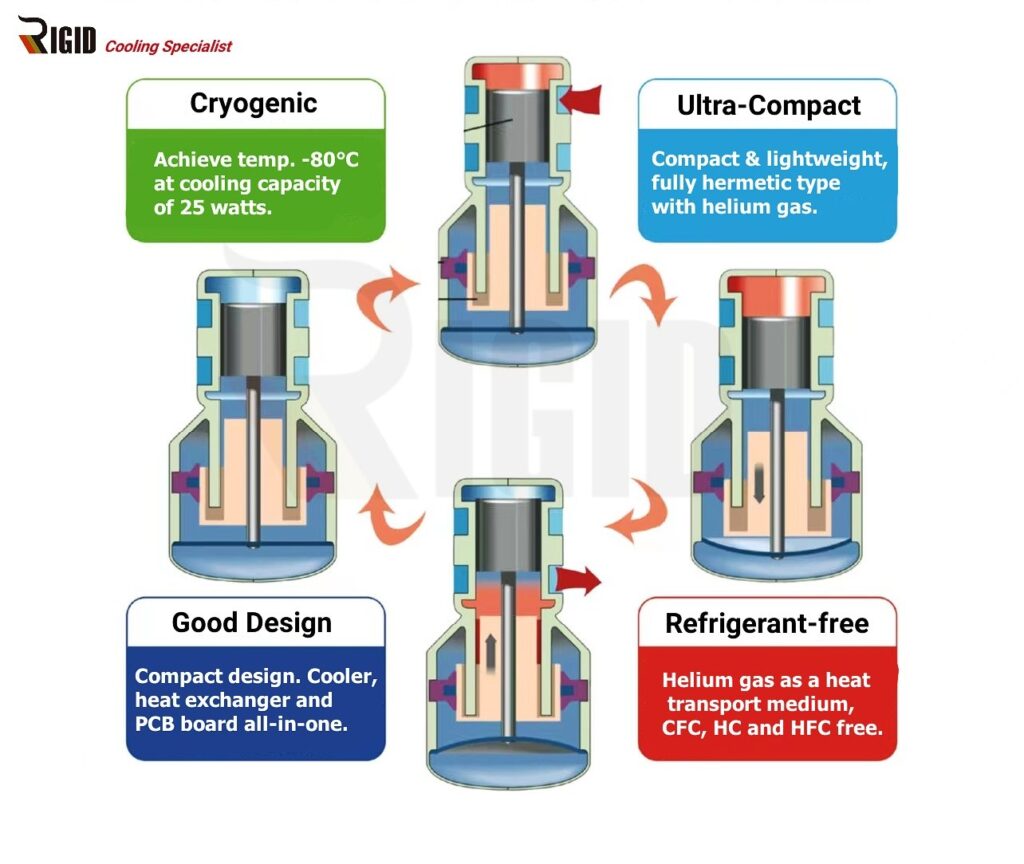
Cryocooler Advantages
Advantages of using a Stirling cooler in this application include:
- High Cooling Efficiency: Stirling coolers can achieve low temperatures efficiently, making them suitable for cryogenic applications.
- Precise Temperature Control: The ability to precisely control and maintain temperatures is crucial for scientific experiments that require specific temperature conditions.
- Low Vibration: Stirling coolers operate with minimal vibration, making them suitable for use in sensitive laboratory equipment where vibration can negatively impact measurements.
- Reliability: Stirling coolers are known for their reliability, providing a stable and continuous cooling solution for scientific instruments.
In a word, the Stirling cooler is chosen for its ability to provide precise and efficient cryogenic cooling, making it well-suited for the requirements of the lab’s tritium measurement analysis machine.
Cryocooler RS100 PLUS
RIGID company Stirling cooler, particularly the RS100PLUS model, plays a pivotal role in various measurement analysis machines in labs. Its primary function is cryogenic cooling, catering to the demanding temperature requirements of liquid and gas sample analysis. With the capability to reach temperatures below -100 degrees Celsius, RIGID company Stirling cooler establishes the essential cold environment necessary for precise sample measurements, enhancing the sensitivity and accuracy of analytical instruments.

A scientific lab in Australia is using Cryocooler to get ultra-low temperatures.
Precise temperature control is a standout feature of Stirling coolers, addressing a critical factor in scientific experiments. The Stirling cycle, the thermodynamic process underlying these coolers, enables meticulous temperature regulation. This control ensures that the analysis machine operates within the specific temperature parameters vital for sample analysis, thereby contributing to the reliability of the obtained results.
Furthermore, the Stirling cooler offers advantages in its compact size and vibration-free operation. In the confined spaces of laboratories, where minimizing vibrations is crucial for sensitive measurements, the compact design and low-vibration characteristics of Stirling coolers make them well-suited for integration into scientific equipment. This design feature safeguards the gas/liquid measurement analysis machine from external factors, preserving the overall reliability of the laboratory setup.
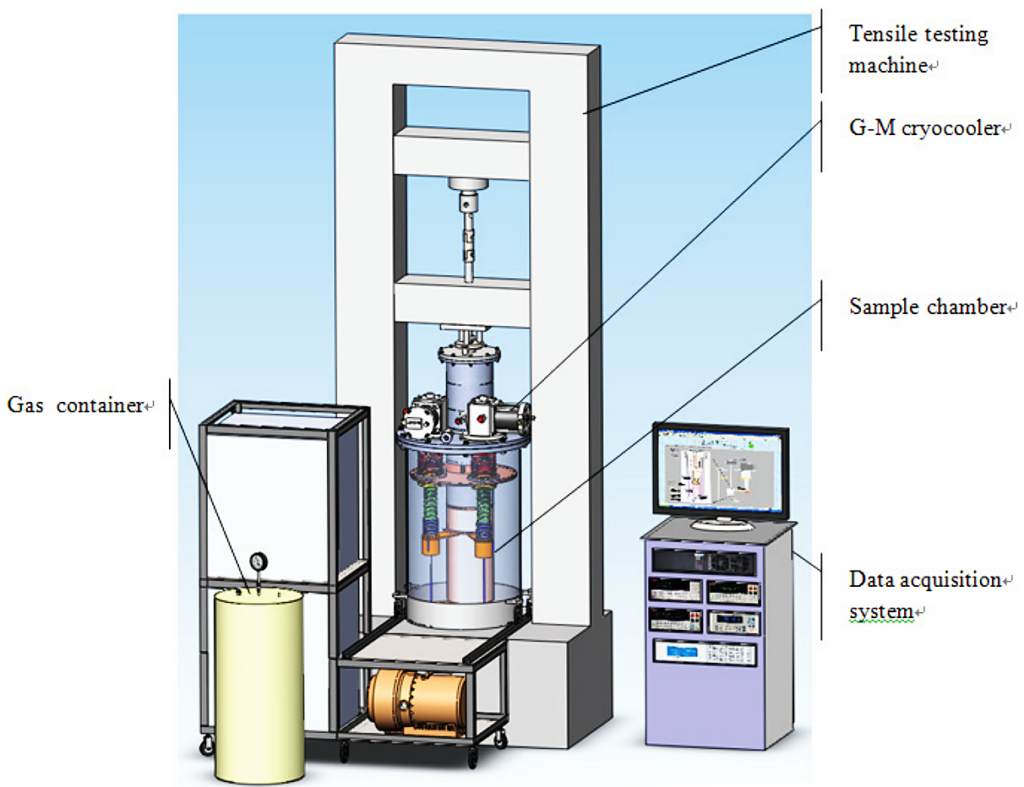
Scheme of the cryogenic mechanical property testing system cooled by a cryocooler.
Reliability is a hallmark attribute of Stirling coolers, exemplified by the RS100PLUS model. Known for its extended operational life and dependable performance, this cooler is ideal for scientific experiments requiring continuous and prolonged cooling. The stability and consistency provided by Stirling coolers position them as a preferred choice in laboratory settings where precision and reliability are paramount considerations.
In summary, the RIGID company Stirling Cryocooler’s multifaceted contributions, ranging from cryogenic cooling to precise temperature control and reliability, make it a crucial component in the success of measurement analysis machines and devices.
Reference Document: FPSC Cryocooler Use in Isotope Analysis

RIGID Company Stirling Cryocooer FPSC

